Logarithm Calculator
Solve Logarithms With Mathematical Precision
Logarithmic Equation Evaluation Process Explained
What Is a Logarithm?
One of the most important questions is answered by a logarithm:
What is the power to be lifted to give a certain number?
Example:
\( \log_{10}(100) = 2 \)
Because \( 10^2 = 100 \).
Logarithms are used to reverse exponentiation. While exponents grow numbers, logs determine the exponent that created them. A log calculator automates this reversal instantly.
Applications of Logarithms
- Algebra
- Calculus
- Statistics
- Finance
- Computer science
Common Types of Logarithms
Common logarithm (base \( 10 \))
Written as \( \log(x) \). Widely used in science and engineering.
Natural logarithm (base \( e \))
Written as \( \ln(x) \). Essential in calculus and exponential growth modeling.
Custom base logarithm
Written as \( \log_{b}(x) \). Used in specialized equations and computer algorithms.
A log calculator evaluates all these types automatically.
Logarithmic Rules and Properties
Logarithms follow structured algebraic rules:
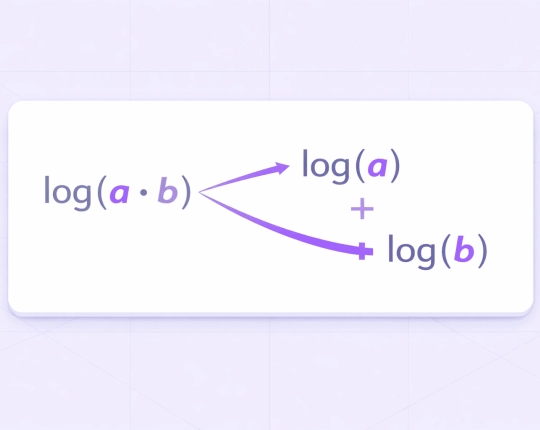
- Product rule
\( \log(a \times b) = \log(a) + \log(b) \) - Quotient rule
\( \log\left(\frac{a}{b}\right) = \log(a) – \log(b) \) - Power rule
\( \log(a^n) = n \cdot \log(a) \) - Change of base rule
\( \log_{b}(x) = \frac{\log(x)}{\log(b)} \)
The calculator applies these properties step by step to simplify complex expressions.

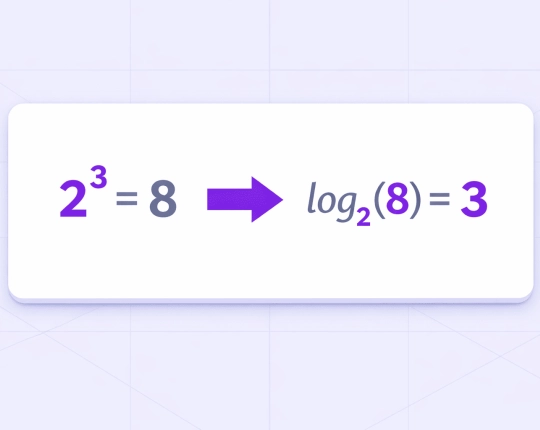
Converting Between Logs and Exponents
All logarithmic equations can be converted into exponential forms.
Example:
\( \log_{2}(8) = 3 \)
Equivalent exponential form:
\( 2^3 = 8 \)
The knowledge of this relationship is useful when working out exponential equations or when analyzing growth models. These conversions are automatically performed with the help of a log calculator.
Solving Logarithmic Equations
Logarithmic equations must first be put into a form with the logarithmic expression isolated, and then converted to exponential form.
Example:
\( \log(x) = 3 \)
Rewrite as:
\( 10^3 = x \rightarrow x = 1000 \)
More complicated equations might require combining logarithms, applying power rules, or simplifying both sides of the equation.
In calculus contexts, solving such equations often integrates with tools like a free derivative calculator when logarithms appear in rate-of-change problems.

Exponential Growth and Logarithms
Logarithms are closely associated with exponential functions.
They appear in:
- Population growth models
- Compound interest calculations
- Radioactive decay
- Algorithm complexity
When exponential curves are analyzed graphically, asymptotic behavior may emerge. In such cases, an asymptotes calculator helps identify long-term boundaries of logarithmic or exponential graphs.
Natural Logarithms in Calculus
Natural logarithms \( \ln(x) \) play a central role in calculus.
They simplify derivatives and integrals that involve exponential functions.
Examples:
\( \frac{d}{dx} \ln(x) = \frac{1}{x} \)
\( \int \frac{1}{x} \, dx = \ln|x| + C \)
Owing to this relationship, logarithmic analysis is often used together with an integral calculator when solving problems involving area or accumulation.

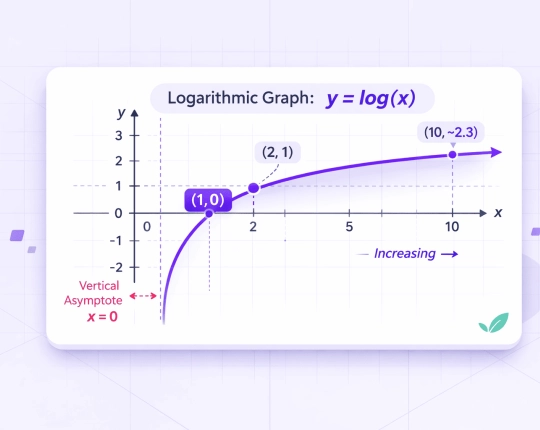
Graph Behavior of Log Functions
Logarithmic graphs share consistent characteristics:
- They pass through \( (1, 0) \).
- They grow slowly compared to exponential functions.
- They never touch the \( y \)-axis.
- The vertical axis \( x = 0 \) is a vertical asymptote because \( \log(0) \) is undefined.
Sample Log Calculation With Clear Steps
Evaluate:
\( \log_{2}(32) \)
Step 1: Convert to exponential form
\( 2^x = 32 \)
Step 2: Identify the exponent
\( 2^5 = 32 \)
Step 3: Final result
\( \log_{2}(32) = 5 \)
A log calculator performs this instantly while explaining each transformation.
Practical Applications of Logarithms
Logarithms appear across many industries:
- Finance
Used in compound interest and investment growth models involving exponential functions such as \( A = P(1 + r)^t \). - Data science
Log scaling such as \( \log(x) \) improves data visualization and handles large-value distributions. - Engineering
Signal strength and decibel calculations rely on logarithmic formulas like \( 10 \log_{10}\left(\frac{P_1}{P_2}\right) \). - Medicine
pH levels use logarithmic concentration scales defined by \( \text{pH} = -\log_{10}[H^+] \). - Computer science
Algorithm complexity often follows patterns such as \( \log(n) \), especially in binary search and divide-and-conquer methods.
Automation through a log calculator ensures precision and efficiency in these domains.

Common Mistakes When Working With Logs
Several recurring issues appear in manual calculations:
- Ignoring log rules
Failing to correctly apply properties such as \( \log(a \times b) = \log(a) + \log(b) \) or \( \log\left(\frac{a}{b}\right) = \log(a) – \log(b) \). - Wrong base interpretation
Confusing natural logarithms \( \ln(x) \) with common logarithms \( \log(x) \) (base \( 10 \)). - Invalid inputs
Logarithms are undefined for negative numbers or zero in the real number system, meaning expressions like \( \log(-5) \) or \( \log(0) \) are not valid. - Conversion errors
Miswriting exponential equivalents, such as incorrectly converting \( \log_{b}(x) = y \) into exponential form \( b^y = x \), leads to incorrect solutions.
A structured log calculator eliminates these risks through rule-based processing.
From Expression Input to Final Log Solution
The calculator performs both symbolic and numerical evaluation of logarithmic expressions.
- First, it identifies the type of logarithm and its base, such as \( \log_{10}(x) \), \( \ln(x) \), or \( \log_{b}(x) \).
- Next, it applies simplification rules including the product, quotient, and power properties like \( \log(a^n) = n \log(a) \).
- When solving equations, it transforms logarithmic equations such as \( \log(x) = 3 \) into exponential form \( 10^3 = x \).
This multi-level processing ensures computational accuracy while reinforcing clear mathematical concepts.
Step-by-Step Solvers for Algebra, Calculus & Geometry
Choose your plan
Free plan
- Unlimited use with ads included
- Free access to all AI tools
- Download all responses (answers, presentations, flashcards, etc.)
- Share responses with others
AI-Plus
- Expert reviews on discounted prices
- Ad-free experience to:
- AI detector
- Diagram generator
- PowerPoint generator
- Answer generator
- Flashcard maker
- Notes generator
- Research assistant
- Download all responses (answers, presentations, flashcards, etc.)
- Share responses with others
- Advanced reasoning
Expert help
- Presentations (human-made)
- Homework help
- STEM support
- Writing assistance
- Editing & proofreading