Long Division Calculator
A Clear Way to Solve Long Division
How to Use the Long Division Calculator

How Long Division Works
Long division is a method that has a set pattern of operations which is generally known in schools. The calculator initially verifies if the divisor can be placed into the current number. If the answer is negative, the following digit is brought down to make a bigger number. This process is continued until the division gives a definite result.
At each point, the calculator figures out the number of times the divisor can be accommodated in the current number. It only then that it puts a digit in the quotient. After multiplication and subtraction, the leftover or remainder is made the new dividend for the following step.
In case the division is not perfect and ends with a remainder, the latter is displayed. Sometimes the calculator decides to proceed with the division by putting a decimal point and thus the calculation is extended.

Long Division With Steps
This calculator shows more than the final answer. Each division step appears in the same order used during manual calculations. You can see when to divide, when to multiply, and when to subtract.
Because the entire process stays visible, it becomes easier to spot mistakes and understand why a result looks the way it does. This makes the tool useful for both checking answers and learning the method.
Components of Long Division
Every long division problem uses the same elements:
- Dividend – the number being divided
- Divisor – the number used to divide
- Quotient – the result of the division
- Remainder – what stays after the final subtraction
Understanding these parts helps make sense of the entire division process, from the first digit to the final result. You might also want to use a fraction calculator to see how the remainder looks when you write it as a proper fraction.
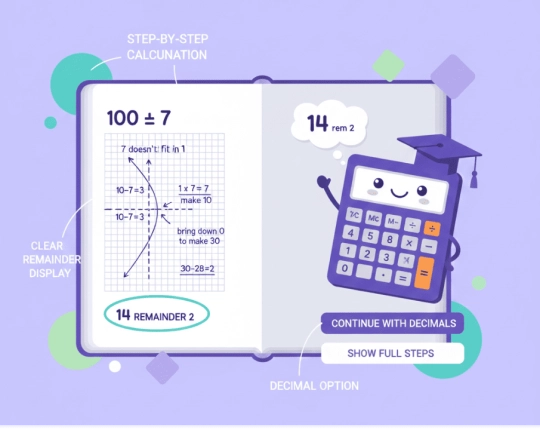
Example: Long Division Step by Step
- For example, divide 100 by 7.
- Since 7 does not fit into 1, the calculator combines digits to form 10.
- 10 divided by 7 gives 1.
- After multiplying and subtracting, the next number becomes 30.
- 30 divided by 7 gives 4, leaving a remainder of 2.
The final result is 14 remainder 2, shown clearly by the calculator.
Long Division With Remainders
Some divisions end with a value that cannot be divided evenly. In such cases, the calculator stops and displays the remainder next to the quotient.
If needed, the calculation can continue by adding decimal places. When a whole-number result is required, the remainder provides a complete and accurate answer without confusion.
Explore More Calculators
Choose your plan
Free plan
- Unlimited use with ads included
- Free access to all AI tools
- Download all responses (answers, presentations, flashcards, etc.)
- Share responses with others
AI-Plus
- Expert reviews on discounted prices
- Ad-free experience to:
- AI detector
- Diagram generator
- PowerPoint generator
- Answer generator
- Flashcard maker
- Notes generator
- Research assistant
- Download all responses (answers, presentations, flashcards, etc.)
- Share responses with others
- Advanced reasoning
Expert help
- Presentations (human-made)
- Homework help
- STEM support
- Writing assistance
- Editing & proofreading