Pythagorean Theorem Calculator
Solve Right Triangle Problems With Confidence
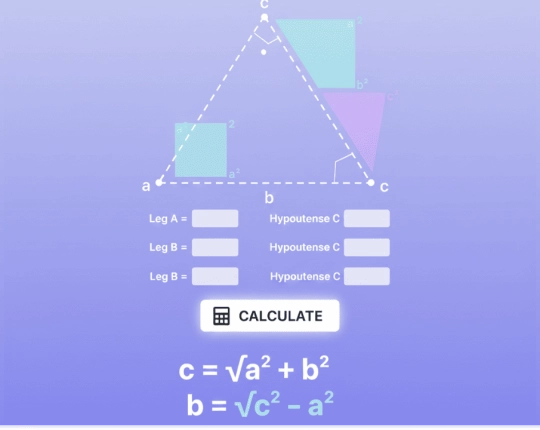
How To Use Pythagorean Theorem Calculator
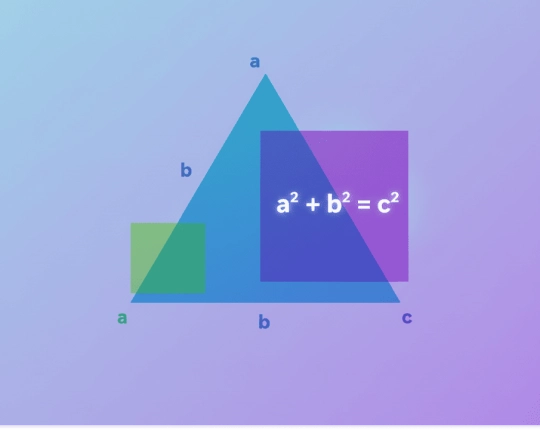
What Is the Pythagorean Theorem?
Pythagorean theorem is an account of a given connection between the three sides of a right triangle. According to it, the square of the longest side is the sum of the squares of the other two sides.
This is because the opposite of the right angle is the longest side, which is referred to as the hypotenuse. The theorem is only applicable to the triangles which have a right angle. In cases where two sides are known the third one could be determined directly.
This connection occurs commonly in geometry, physics, and projects where an ai physics diagram generator maps out the dimensions.
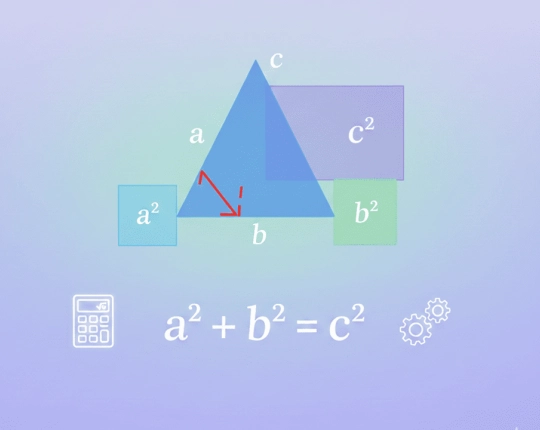
The Pythagorean Theorem Formula
The formula is written as:
a² + b² = c²
The right angle of the legs is a and b, and the hypotenuse is c in this case.
The formula can be rearranged to solve the value of either side of the equation depending on the missing term.
Using square root, addition or subtraction and then square root is to be use to ensure consistency and reliability.
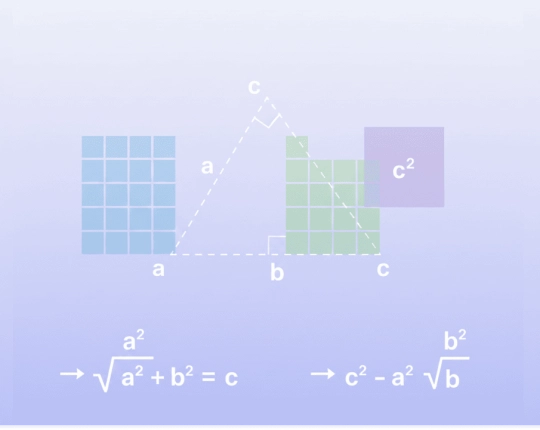
How to Use the Pythagorean Theorem
Finding the hypotenuse
Divide both legs into squares, sum the numbers and find the square root. The longitudinal is never the shortest side.
Finding a missing leg
Squared the hypotenuse, minus square of known leg, square root. This provides the length of the lost leg.
The two are effective only in cases where the triangle is at a right angle.
Step-by-Step Example
Take a right triangle, whose legs are 3 and 4 units.
Square the sides:
3² = 9
4² = 16
Add the values:
9 + 16 = 25
Take the square root:
√25 = 5
The hypotenuse equals 5. This example shows how the theorem works in a clear and practical way.
Right Triangle Conditions
The Pythagorean theorem applies only to right triangles. If the triangle does not include a right angle, the formula will not produce a valid result.
Unit consistency also matters. Mixing units such as meters and centimeters leads to incorrect outcomes. In real measurements, rounding can slightly affect precision.
Pythagorean Triples
Pythagorean triples are sets of whole numbers that satisfy the theorem exactly.
Common examples include:
- 3, 4, 5
- 5, 12, 13
These values are useful because they avoid decimals and make calculations faster and more precise.
Related Triangle Calculations
The pythagorean theorem alone is not able to solve some problems. Trigonometric functions like sine might be necessary when a triangle has got one angle and a side. These techniques are of trigonometry, and are not limited to simple geometry.
You can also have to work out area or perimeter. These tasks can be assisted by other tools and calculators in case of need of more information. Besides this tool, you can use an AI homework helper to work out area or perimeter.
Explore More Calculators
Choose your plan
Free plan
- Unlimited use with ads included
- Free access to all AI tools
- Download all responses (answers, presentations, flashcards, etc.)
- Share responses with others
AI-Plus
- Expert reviews on discounted prices
- Ad-free experience to:
- AI detector
- Diagram generator
- PowerPoint generator
- Answer generator
- Flashcard maker
- Notes generator
- Research assistant
- Download all responses (answers, presentations, flashcards, etc.)
- Share responses with others
- Advanced reasoning
Expert help
- Presentations (human-made)
- Homework help
- STEM support
- Writing assistance
- Editing & proofreading