Sequence Calculator
Analyze Sequences With Mathematical Accuracy
Using the Sequence Calculator Step by Step
Logic That Defines a Sequence
A sequence is a list of numbers in a particular order and following a special rule or pattern. Each number in the list is known as a term, and its position defines its value.
Example:
\( 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, \dots \)
Each term increases by \( 2 \). This consistent structure allows mathematicians to predict future values without listing every step.
Sequences appear throughout many branches of mathematics and applied sciences — from algebra and calculus to computer science and financial modeling. Getting familiar with how they function is important because they form the foundation for more advanced concepts, such as limits and infinite series.

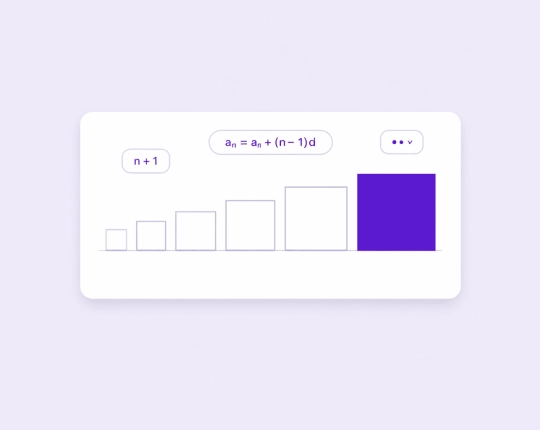
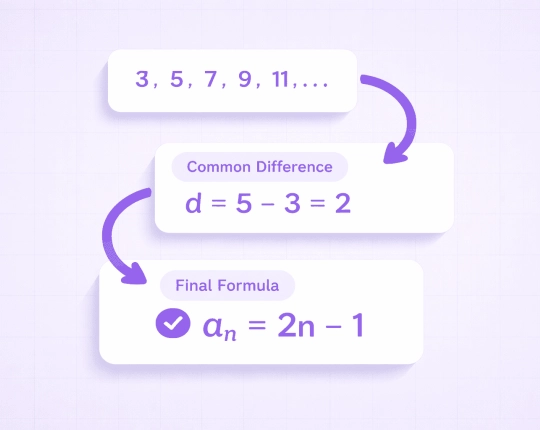
Arithmetic Sequences Explained
An arithmetic sequence is one in which the difference between consecutive terms remains a constant difference.
Example:
\( 5, 9, 13, 17, \dots \)
Here, the common difference equals \( 4 \).
To mathematically describe this progression, we apply the arithmetic sequence formula:
\( a_n = a_1 + (n – 1)d \)
Where:
- \( a_n \) = nth term
- \( a_1 \) = first term
- \( d \) = common difference
- \( n \) = term position
A sequence calculator applies this formula automatically to generate any requested term.
Finding Missing Terms
One of the most practical uses of a sequence calculator is filling gaps in partially known sequences.
If you know:
- First term
- Common difference
- Position of the term
The missing term is calculated by the calculator instantly.
This is particularly useful in exams, validation of homework, and long-range projections, which are time-consuming to do manually.
Explicit vs Recursive Formulas
Sequences can be expressed in two primary ways:
- Explicit formula
Directly calculates any term using its position.
Example: \( a_n = 3n + 1 \) - Recursive formula
Defines each term using the previous one.
Example: \( a_n = a_{n-1} + 3 \)
The calculator can interpret both approaches and convert recursive patterns into explicit forms for easier analysis.
Sequence Growth and Behavior
Sequences do not increase at a constant rate. Arithmetic sequences grow in a linear way whereas a geometric sequence grows multiplicatively, usually forming more elaborate designs as time progresses.
With other forms of sequences, they might increase faster, slower or even tend to approach one particular limit and get nearer and nearer to it. To further analyze the results, they can be connected with such tools as a free limit calculator to study long-term behavior.
The identification of these growth patterns is of particular significance to areas like calculus, economics and the analysis of the efficiency of algorithms.
Sequences and Series Connection
When you add the terms of a sequence, you create a series.
Example:
Example sequence:
\( 2, 4, 6, 8, \dots \)
Corresponding series:
\( 2 + 4 + 6 + 8 + \dots \)
To compute totals efficiently, many users pair the sequence calculator with a sum of series calculator, which evaluates finite or infinite sums using formal summation formulas.
This relationship bridges algebra and calculus concepts.
Finite vs Infinite Sequences
- Finite sequences
Contain a fixed number of terms and stop at a specific point. - Infinite sequences
Continue indefinitely without an endpoint.
This analysis becomes foundational in calculus and real analysis.
Exponential and Non-Linear Sequences
Some sequences do not grow by addition but by multiplication. These follow exponential rules rather than arithmetic ones.
Example:
\( 2, 4, 8, 16, 32, \dots \)
Each term doubles.
To evaluate such patterns, integration with an exponential function calculator helps model growth curves, decay rates, and compounding processes.
These sequences appear in:
- Population growth
- Investment returns
- Radioactive decay
- Algorithm complexity

Worked Example With Full Calculation Steps
Consider the sequence:
\( 7, 11, 15, 19, \dots \)
Step 1: Identify the common difference
\( 11 – 7 = 4 \)
Step 2: Apply the formula
\( a_n = 7 + (n – 1)4 \)
Step 3: Find the 10th term
\( a_{10} = 7 + 9 \times 4 = 43 \)
A sequence calculator performs this instantly while displaying the formula and logic.
Practical Applications of Sequences
Sequences extend far beyond academic exercises.
- Finance
Loan payments and savings schedules often follow arithmetic or exponential patterns. - Computer science
Algorithms use sequences to measure performance growth. - Physics
Motion, wave frequencies, and quantum states rely on ordered numeric progressions. - Data science
Trend modeling and forecasting depend on sequence behavior.
Using a sequence calculator accelerates these evaluations while minimizing human error.

Common Mistakes When Working With Sequences
Several recurring errors affect sequence calculations:
- Misidentifying the pattern
Confusing arithmetic and exponential growth leads to incorrect formulas. - Wrong term indexing
Forgetting that sequences often start at \( n = 1 \) shifts all results. - Incorrect difference calculation
A small subtraction mistake changes the entire sequence.
Automation through a sequence calculator eliminates these structural mistakes.
The Logic Behind the Sequence Calculator Engine
The calculator begins by analyzing input values to detect structural patterns. It evaluates differences, ratios, and positional relationships.
Next, it generates:
- Explicit formulas
- Missing terms
- Term positions
- Growth patterns
This layered computation ensures both accuracy and educational transparency.
Step-by-Step Solvers for Algebra, Calculus & Geometry
Choose your plan
Free plan
- Unlimited use with ads included
- Free access to all AI tools
- Download all responses (answers, presentations, flashcards, etc.)
- Share responses with others
AI-Plus
- Expert reviews on discounted prices
- Ad-free experience to:
- AI detector
- Diagram generator
- PowerPoint generator
- Answer generator
- Flashcard maker
- Notes generator
- Research assistant
- Download all responses (answers, presentations, flashcards, etc.)
- Share responses with others
- Advanced reasoning
Expert help
- Presentations (human-made)
- Homework help
- STEM support
- Writing assistance
- Editing & proofreading