Simplify Calculator
Simplify Math Expressions With Accuracy
How to Use the Simplify Calculator
What Does It Mean to Simplify an Expression?
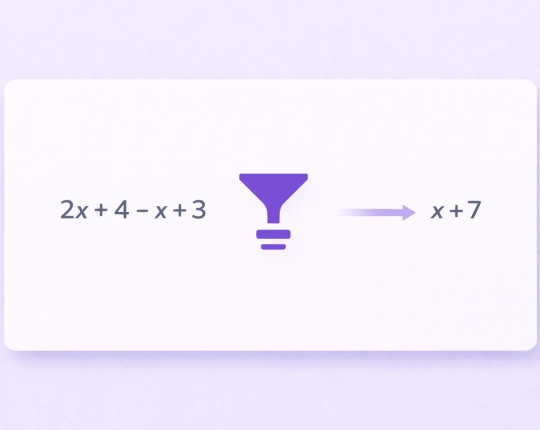
The simplification of an expression is the process of rewriting an expression in the simplest and most readable form possible without alteration of its value. This can be done by grouping similar words and phrases, fractions, number factoring, and rationalization of denominations.
For example:
- 2x + 3x simplifies to 5x
- 6/12 simplifies to 1/2
- √50 simplifies to 5√2
The aim is always directness and effectiveness. An uncomplicated outcome is more accessible to interpretation, further computation, or implementation in equations.
Types of Problems a Simplify Calculator Solves
A calculator of the modern era has a broad variety of mathematical operations:
- Fractions
It decomposes fractions to the lowest terms by identifying shared factors. In cases of necessity, it is in collaboration with a free fraction calculator, which is used to convert improper fractions or mixed numbers. - Algebraic expressions
Coefficients and variables are simplified to a poly-form. - Radicals
Square roots and higher radicals decrease the extracting of perfect powers. - Exponents
The rules of operations of powers include multiplication, division, and negative exponents. - Complex expressions
Multi-step expressions simplify by using the order of operations and factor cancellation.
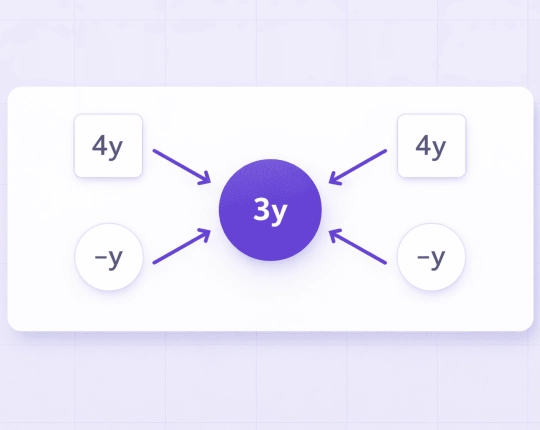
Simplifying Fractions
One of the most typical use cases is that of fraction simplification. The calculator determines the greatest common divisor (GCD) shared by both the numerator and denominator. It then divides the numerator and denominator by the same value to reduce the fraction to its lowest terms.
Example:
18/24 → divide by 6 → 3/4
In cases where the variables or a given polynomial are present in fractions, the calculator factors then reduces the parts. This is related directly to techniques in a factoring calculator, particularly with algebraic fractions.
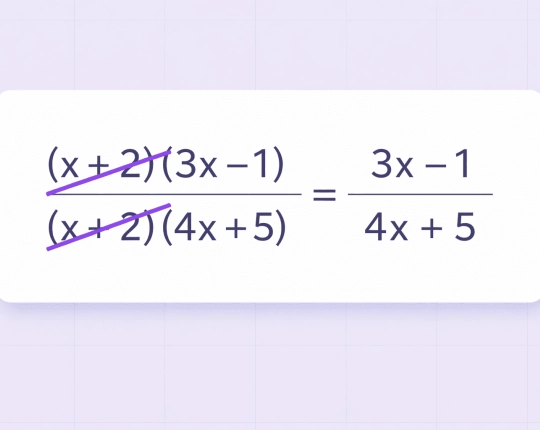
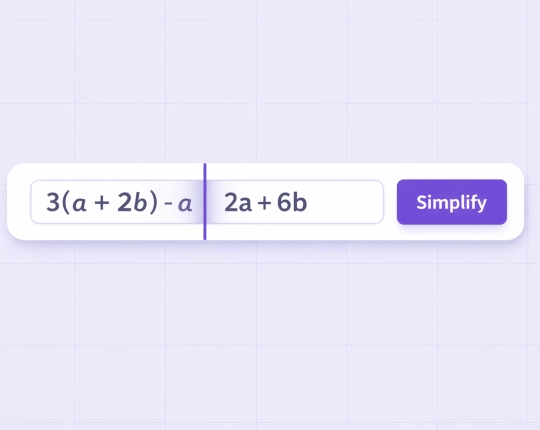
Simplifying Algebraic Expressions
Algebraic simplification focuses on combining like terms and reducing polynomial structures.
Example:
4x + 7x − 2x = 9x
When expressions grow more complex, factoring becomes essential. The calculator may extract common factors or apply identities such as:
- Difference of squares
- Perfect square trinomials
- Quadratic factorization
Radicals and Roots Simplification
Radicals simplify by extracting perfect squares or higher powers.
Example:
\( \sqrt{72} = \sqrt{36 \times 2} = 6\sqrt{2} \)
The calculator automatically detects factorable components inside the radical. This avoids manual trial-and-error and ensures correct reduction.
Radical simplification often appears in geometry, physics, and engineering formulas where exact values matter more than decimals.
Exponents and Powers
Expressions with exponents follow strict mathematical laws:
- \( a^m \times a^n = a^{m+n} \)
- \( a^m \div a^n = a^{m-n} \)
- \( (a^m)^n = a^{mn} \)
The simplify calculator applies these automatically, reducing expressions into compact exponential form.
This becomes especially useful in calculus, scientific notation, and algebraic modeling.
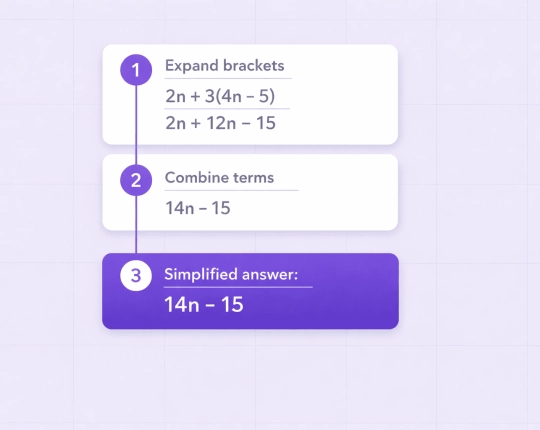
Order of Operations in Simplification
Complex expressions require structured evaluation using PEMDAS/BODMAS rules:
- Parentheses
- Exponents
- Multiplication and division
- Addition and subtraction
The calculator follows this hierarchy precisely. It may also integrate polynomial reduction, fraction simplification, or factoring at intermediate steps.
When division appears inside algebraic simplification, logic similar to a long division calculator may apply, particularly for polynomial division.
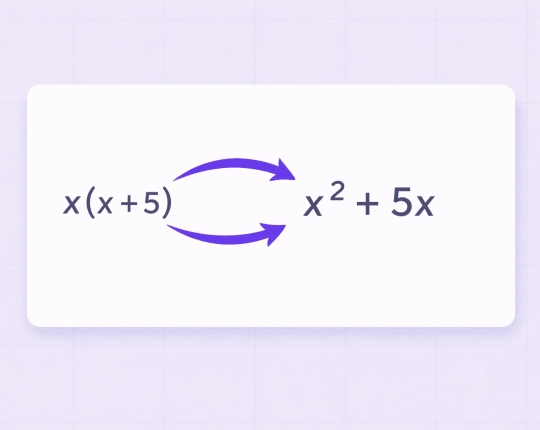
AI-Enhanced Simplification
Modern tools extend beyond static math engines. An AI math solver can interpret expressions written in natural input, scanned text, or complex notation.
AI support enables:
- Expression recognition
- Step explanations
- Method comparisons
- Error detection
By combining symbolic algebra with AI reasoning, simplification becomes both computational and educational.
Practical Applications of Simplification
Simplification is not limited to classroom exercises. It appears in:
- Equation solving
Simplified expressions make isolating variables easier. - Engineering formulas
Reduced equations improve readability and reduce substitution errors. - Finance calculations
Interest formulas and ratios often simplify before evaluation. - Physics problems
Distance, velocity, and force equations rely on algebraic reduction. - Data modeling
Statistical and exponential expressions require simplification before interpretation.

Common Mistakes When Simplifying
Students and professionals alike make recurring simplification errors:
- Incorrect factor cancellation
Cancelling terms that are added rather than multiplied leads to wrong results. - Sign errors
Negative values often flip during factoring or distribution. - Partial simplification
Stopping before full reduction leaves expressions unnecessarily complex. - Exponent misrules
Confusing multiplication and power rules produces invalid answers.
A structured simplify calculator prevents these issues by applying validated algebraic logic.

How the Simplify Calculator Works
The calculator processes expressions through symbolic algebra systems. It first parses the structure of the input, identifying numbers, variables, operators, and grouping symbols.
Next, it applies simplification layers:
- Combine like terms
- Reduce fractions
- Factor expressions
- Simplify radicals
- Apply exponent laws
Advanced Math Tools
Choose your plan
Free plan
- Unlimited use with ads included
- Free access to all AI tools
- Download all responses (answers, presentations, flashcards, etc.)
- Share responses with others
AI-Plus
- Expert reviews on discounted prices
- Ad-free experience to:
- AI detector
- Diagram generator
- PowerPoint generator
- Answer generator
- Flashcard maker
- Notes generator
- Research assistant
- Download all responses (answers, presentations, flashcards, etc.)
- Share responses with others
- Advanced reasoning
Expert help
- Presentations (human-made)
- Homework help
- STEM support
- Writing assistance
- Editing & proofreading