Square Root Calculator
Calculate Square Roots With Precision
Square Root Calculator User Guide

Definition of a Square Root in Mathematics
A square root is the number such that when it is multiplied by itself will give the same value.
Example:
\( \sqrt{25} = 5 \)
Because \( 5 \times 5 = 25 \).
Square roots prove to be fundamental in algebra, geometry, and applied sciences, and create an inverse of squaring. It is automated by a square root calculator that does not compromise mathematical accuracy.
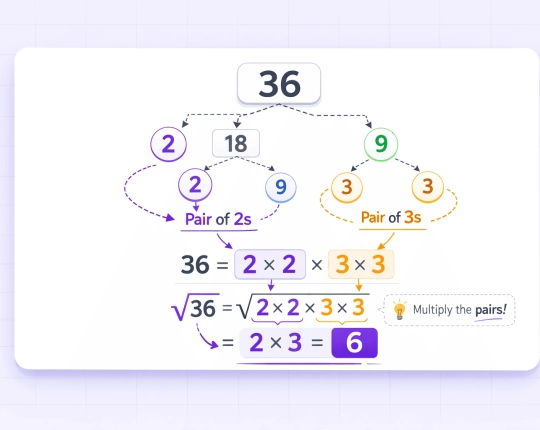
Perfect vs Non-Perfect Squares
- Perfect squares
Numbers \( 4 \), \( 9 \), \( 16 \), and \( 36 \) are roots of whole numbers.
Example: \( \sqrt{36} = 6 \) - Non-perfect squares
The numbers that have irrational roots are \( 7 \), \( 10 \), or \( 50 \).
Example: \( \sqrt{10} \approx 3.162 \)
These values are given in radical and in decimal form using the calculator.

Simplifying Square Roots
It is possible to simplify some roots that are not necessarily perfect squares.
Example:
\( \sqrt{72} = \sqrt{36 \times 2} = 6\sqrt{2} \)
The calculator enters the number and extracts perfect square factors automatically. This type of simplification is essential in algebraic manipulation and geometric formulas.
Square Roots in Geometry
Square roots are commonly used in geometrical calculations, especially in right triangles.
By application of the Pythagorean theorem:
\( a^2 + b^2 = c^2 \)
To determine \( c \), we compute:
\( c = \sqrt{a^2 + b^2} \)
Such tools as a Pythagorean theorem calculator directly rely on square root calculations to determine the sides of a triangle.
Distance formulas, diagonal measurements, and vector magnitudes also depend on accurate root evaluation.
Square Roots in Quadratic Equations
Quadratic equations often require square roots to solve for unknown variables.
Example:
\( x = \frac{-b \pm \sqrt{b^2 – 4ac}}{2a} \)
The discriminant under the radical determines the solution type. A quadratic formula calculator integrates square root logic to compute real or complex solutions efficiently.
Without root simplification, quadratic solving becomes impractical for large or irregular coefficients.
Numbers and Roots of Irrational Order
The calculator preserves exact notation using the square root symbol instead of converting values only into decimals. The number of square roots that are irrational (that is, not decimals containing repeats and termination points) is numerous.
Example:
\( \sqrt{2} = 1.414213\ldots \)
These values are not expressible as simple fractions. When necessary, they are computed with an approximation to the desired precision, but in a square root calculator with an exact radical notation.
This bi-representation promotes scholarly excellence as well as measurement.

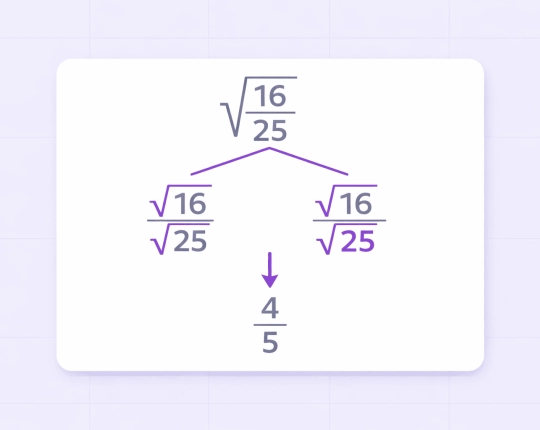
Square Roots of Decimals and Fractions
Roots are not restricted to whole numbers only.
Example:
Example with decimals:
\( \sqrt{0.25} = 0.5 \)
Example:
Example with fractions:
\( \sqrt{\frac{9}{16}} = \frac{3}{4} \)
The calculator converts decimals into fractions where helpful, simplifies numerator and denominator roots, and returns clean final results.
Square Roots in Complex Numbers
When a negative number appears under a square root, the result enters the complex number system.
Example:
\( \sqrt{-9} = 3i \)
These roots contain imaginary number units, which cannot be plotted on the real number line. This process is extended by a complex number calculator, which also works with imaginary roots and complex roots.
These are necessary in electrical engineering, signal processing, and advanced physics.
Example With Full Solution Steps
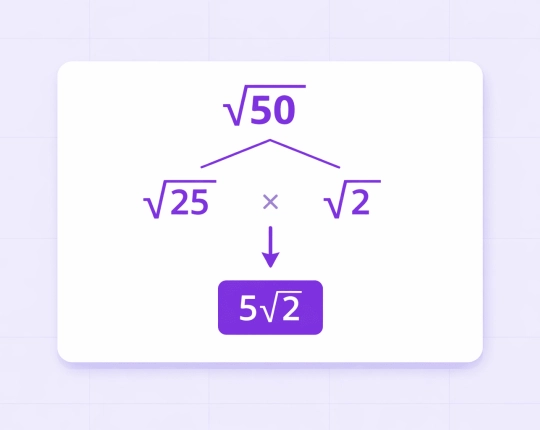
Find \( \sqrt{50} \).
Step 1: Factor the number
\( 50 = 25 \times 2 \)
Step 2: Extract a perfect square
\( \sqrt{25} = 5 \)
Step 3: Simplify
\( \sqrt{50} = 5\sqrt{2} \)
Step 4: Decimal approximation
\( \sqrt{50} \approx 7.071 \)
A square root calculator is fully automated so that both the exact and approximate expressions are presented.

Some Applications of Square Roots
The use of square roots is found in numerous fields in reality.
- Architecture and construction
Used in diagonal and structural measurements. - Physics
Velocity, energy, and wave calculations rely on roots. - Finance
Standard deviation and volatility formulas include root operations. - Computer graphics
Distance rendering and vector normalization depend on square roots. - Engineering
Any of these situations is enhanced by automation via the use of a square root calculator to achieve increased speed and accuracy.
Common Mistakes When Calculating Roots
Several errors appear frequently in manual calculations:
- Ignoring simplification
Failing to extract perfect squares leads to incomplete answers. - Rounding too early
Premature decimal rounding reduces accuracy. - Mishandling negatives
Forgetting imaginary units causes invalid results. - Unit inconsistency
Square roots of measured values must maintain unit logic.
A structured calculator eliminates these issues through rule-based processing.

How the Square Root Calculator Works
The calculator uses layered computation to estimate square roots.
First, it checks whether the number is a perfect square. If not, it factors the value to extract simplifiable components.
Next, it computes decimal approximations using iterative numerical methods. For negative inputs, it transitions into imaginary number logic.
When deeper interpretation is required, a math AI solver explains simplification paths, approximations, and symbolic transformations step by step.
This integration ensures both computational accuracy and conceptual clarity.
Explore More Calculators
Choose your plan
Free plan
- Unlimited use with ads included
- Free access to all AI tools
- Download all responses (answers, presentations, flashcards, etc.)
- Share responses with others
AI-Plus
- Expert reviews on discounted prices
- Ad-free experience to:
- AI detector
- Diagram generator
- PowerPoint generator
- Answer generator
- Flashcard maker
- Notes generator
- Research assistant
- Download all responses (answers, presentations, flashcards, etc.)
- Share responses with others
- Advanced reasoning
Expert help
- Presentations (human-made)
- Homework help
- STEM support
- Writing assistance
- Editing & proofreading